In Agile development, the role of a Scrum Master is central to ensuring a smooth, productive workflow within Scrum teams. Acting as a servant leader, the Scrum Master guides teams through the principles and practices of Scrum, fostering an environment of continuous improvement, collaboration, and transparency. This role, however, goes beyond simply facilitating meetings and overseeing processes; it comes with its own unique challenges and key responsibilities that require a blend of leadership, empathy, and adaptability.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the core responsibilities of a Scrum Master and the challenges they face, highlighting why this role is essential for Agile teams and overall project success.
Understanding the Scrum Master Role
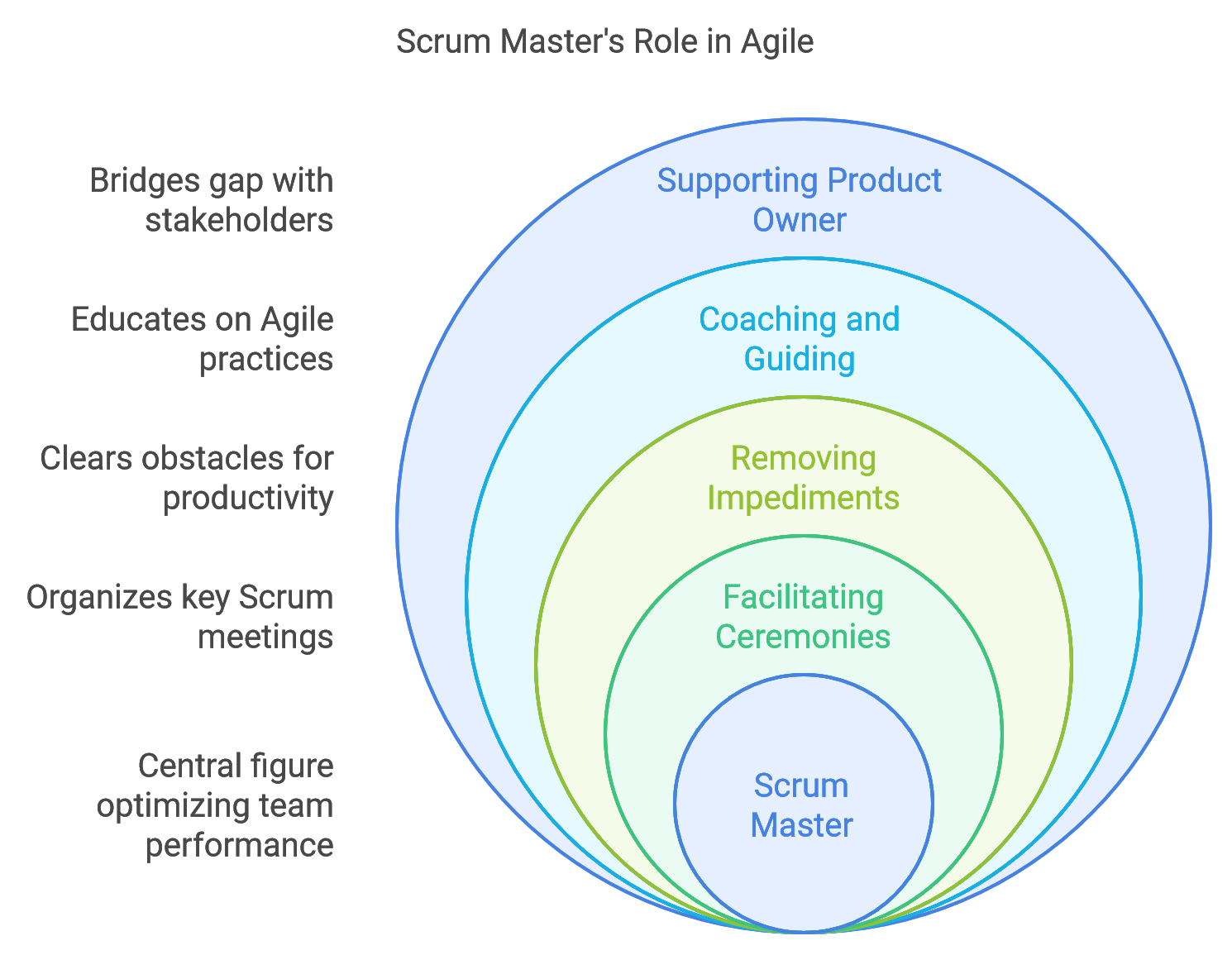
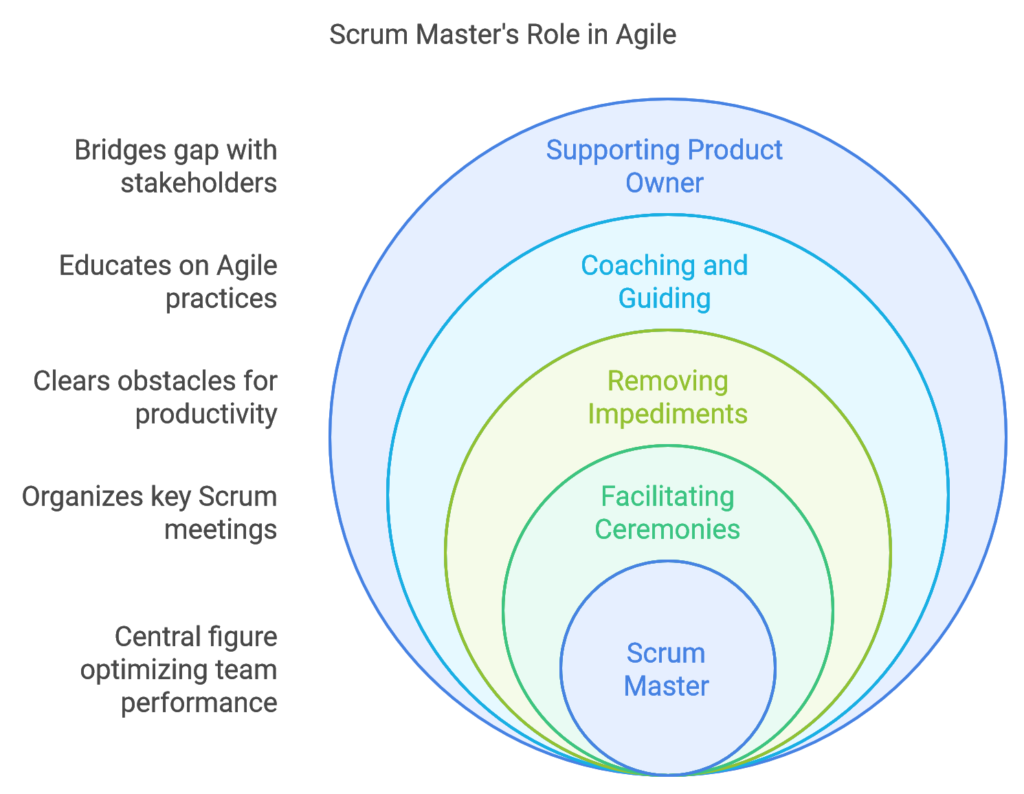
A Scrum Master is responsible for managing the Scrum process within a team, ensuring that it’s followed correctly while helping the team achieve their highest potential. Unlike traditional project managers, Scrum Masters do not dictate tasks; instead, they empower teams to self-organize, remove obstacles, and guide them in adhering to Agile principles. Their ultimate goal is to optimize team productivity and foster an environment of accountability and growth.
Let’s explore the key responsibilities of a Scrum Master.
Key Responsibilities of a Scrum Master
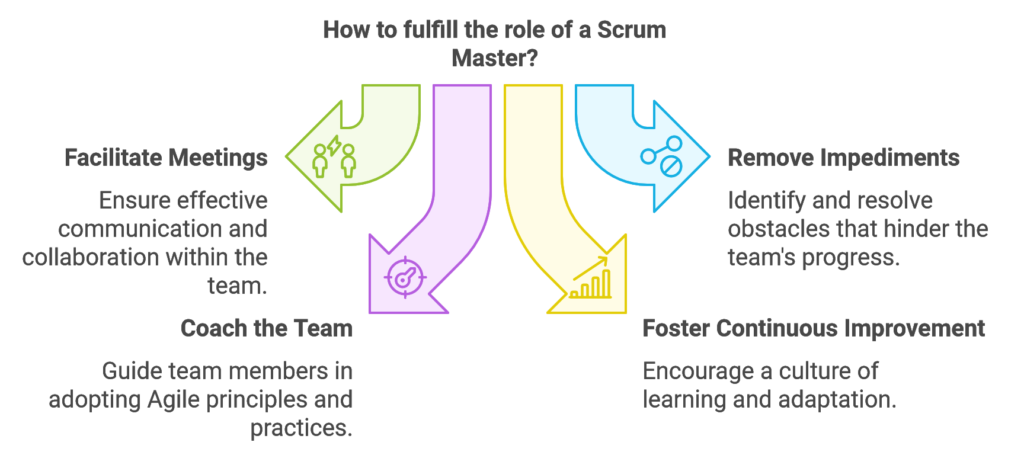
1. Facilitating Scrum Ceremonies
Scrum Masters are responsible for organizing and facilitating key Scrum ceremonies, such as:
- Sprint Planning: Helps the team define sprint goals and prioritize tasks based on the product backlog.
- Daily Stand-ups: Conducts short, daily meetings to track progress and identify blockers.
- Sprint Reviews: Facilitates the presentation of completed work to stakeholders for feedback.
- Sprint Retrospectives: Encourages the team to reflect on the sprint, identifying areas of improvement and recognizing achievements.
Each of these meetings is designed to ensure alignment, transparency, and continuous improvement.
2. Removing Impediments
Scrum Masters work proactively to identify and remove obstacles that hinder team productivity. This could range from technical challenges to interpersonal conflicts or even organizational obstacles that may impact the team’s focus. By clearing these blockers, Scrum Masters enable the team to stay on track and focus on delivering value.
3. Coaching and Guiding the Team in Agile Practices
A key responsibility of the Scrum Master is to coach team members in Agile practices, principles, and values. This includes helping new members understand Scrum, supporting the team in adopting Agile behaviors, and encouraging collaboration and accountability. The Scrum Master ensures that everyone is aligned with the Agile mindset, which is crucial for the team’s long-term success.
4. Supporting the Product Owner
The Scrum Master also collaborates closely with the Product Owner, helping them manage and prioritize the product backlog. They ensure that the team understands the Product Owner’s vision and goals, fostering a transparent communication channel. By supporting the Product Owner, Scrum Masters help bridge the gap between the development team and stakeholders, ensuring alignment on project objectives.
5. Fostering a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is at the heart of Agile, and Scrum Masters play a vital role in cultivating this culture. During retrospectives, the Scrum Master encourages team members to reflect on their performance, identify areas for improvement, and propose actionable changes. They also monitor the effectiveness of these changes and provide support as the team implements new practices.
6. Protecting the Team from Distractions
The Scrum Master is responsible for creating a protective boundary around the team, shielding them from distractions, unnecessary requests, or additional tasks that may disrupt their focus. This is particularly important when working within complex or highly matrixed organizations, where competing priorities can impede the team’s ability to complete their sprint goals.
7. Monitoring Team Performance
Scrum Masters often track performance metrics to identify trends and support team improvement. While they are not responsible for evaluating individual performance, they may monitor metrics such as sprint velocity, cycle time, and burndown charts to gain insight into team productivity. These insights help Scrum Masters identify potential areas for improvement and guide the team toward more effective practices.
Challenges Faced by Scrum Masters
While the role of a Scrum Master is rewarding, it is not without its challenges. Here are some common obstacles Scrum Masters encounter and tips for overcoming them.
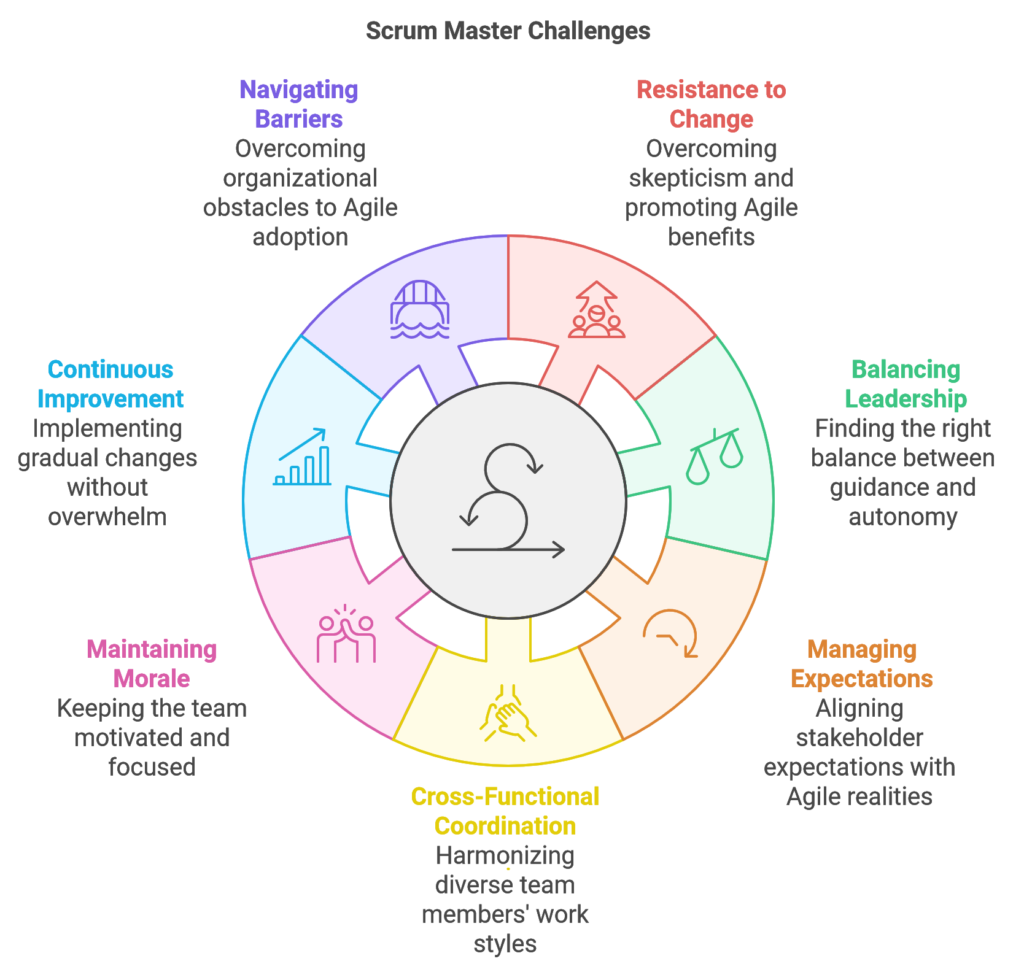
1. Resistance to Change
Transitioning to Agile can be difficult, especially for teams accustomed to traditional project management methods. Scrum Masters often face resistance from team members, stakeholders, or even management who may be skeptical of Agile practices. To address this, Scrum Masters must exhibit patience, educate the team on Agile’s long-term benefits, and demonstrate the value of Scrum practices through consistent results.
2. Balancing the Role of a Servant Leader
Scrum Masters are expected to lead without exerting authority, which can be challenging. They must strike a balance between guiding the team and allowing them to make decisions autonomously. A successful Scrum Master knows when to step in to help and when to step back, fostering a team environment that values self-organization.
3. Handling Stakeholder Expectations
Stakeholders may have unrealistic expectations regarding timelines, project scope, or deliverables. Scrum Masters are responsible for managing these expectations and communicating the iterative nature of Agile development. They work closely with the Product Owner to set realistic timelines and ensure stakeholders understand the importance of flexibility in Agile.
4. Dealing with Cross-Functional Teams
Scrum Masters often manage teams with members from various departments or disciplines, each with its own work style, expectations, and priorities. Coordinating such diverse teams requires excellent communication skills, adaptability, and a collaborative approach. Scrum Masters must foster mutual respect, encourage open communication, and create a shared vision to align cross-functional teams.
5. Maintaining Team Morale and Motivation
Scrum Masters play a critical role in maintaining team morale, especially during challenging sprints or setbacks. It’s their responsibility to provide encouragement, celebrate achievements, and address any issues that may impact team dynamics. A motivated team is more likely to overcome challenges, remain focused, and deliver high-quality results.
6. Ensuring Continuous Improvement without Overloading the Team
Scrum Masters must walk a fine line between driving continuous improvement and overburdening the team with too many changes at once. They should introduce changes gradually, ensuring the team can adopt new practices without feeling overwhelmed. Building a culture of steady, incremental improvement is key to sustainable progress.
7. Navigating Organizational Barriers
In larger organizations, Scrum Masters often face barriers due to legacy systems, rigid structures, or conflicting priorities from other departments. These barriers can hinder Agile adoption and impede the team’s progress. Scrum Masters must collaborate with organizational leaders, advocate for Agile practices, and work to align team goals with the company’s broader objectives.
Essential Qualities of an Effective Scrum Master
To succeed in this challenging role, a Scrum Master must cultivate several key qualities, including:
- Empathy: Understanding the needs and challenges of each team member fosters trust and collaboration.
- Patience: Change takes time, especially when introducing Agile practices to a team or organization.
- Communication Skills: A Scrum Master must be able to convey ideas clearly and facilitate open dialogue within the team.
- Adaptability: Every team and project is unique, and the Scrum Master should be flexible in their approach.
- Conflict Resolution: Addressing conflicts constructively helps maintain a positive, productive team environment.
Conclusion: The Impact of an Effective Scrum Master
The role of a Scrum Master is vital to the success of Agile teams. By fostering collaboration, removing obstacles, and guiding teams in Agile practices, Scrum Masters enable teams to focus on delivering value and achieving continuous improvement. Despite the challenges, a skilled Scrum Master can drive positive change within the organization, helping teams work more efficiently, embrace adaptability, and align with the principles of Agile.
An effective Scrum Master doesn’t just manage processes—they inspire teams to reach their full potential, bridging the gap between traditional management and Agile leadership. For companies committed to Agile, investing in strong Scrum Masters is an investment in the resilience, flexibility, and success of their projects.