In recent years, cloud computing has revolutionized the IT landscape, becoming an essential component of modern business strategies. This technology allows companies to access computing resources over the internet, scaling up or down as needed, without the need to manage physical hardware. The three giants in this space are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll explore what cloud computing is, its benefits, and how AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure compare.
What Is Cloud Computing?
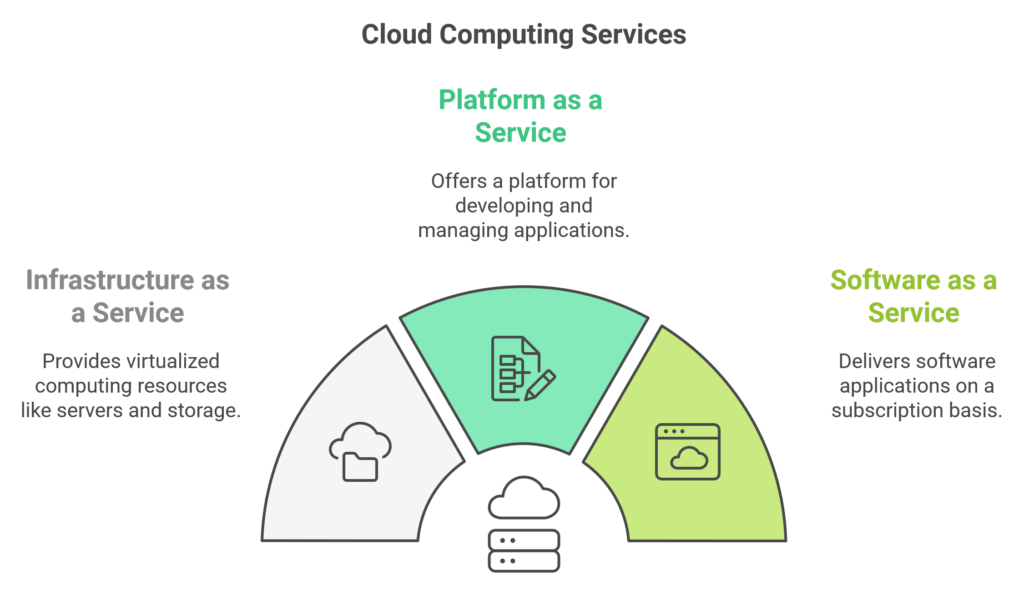
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of various services over the internet, including:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Offers virtualized computing resources over the internet, such as servers and storage.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis.
By using cloud services, businesses can access technology resources on demand, paying only for what they use and avoiding the overhead costs of setting up and maintaining physical servers.
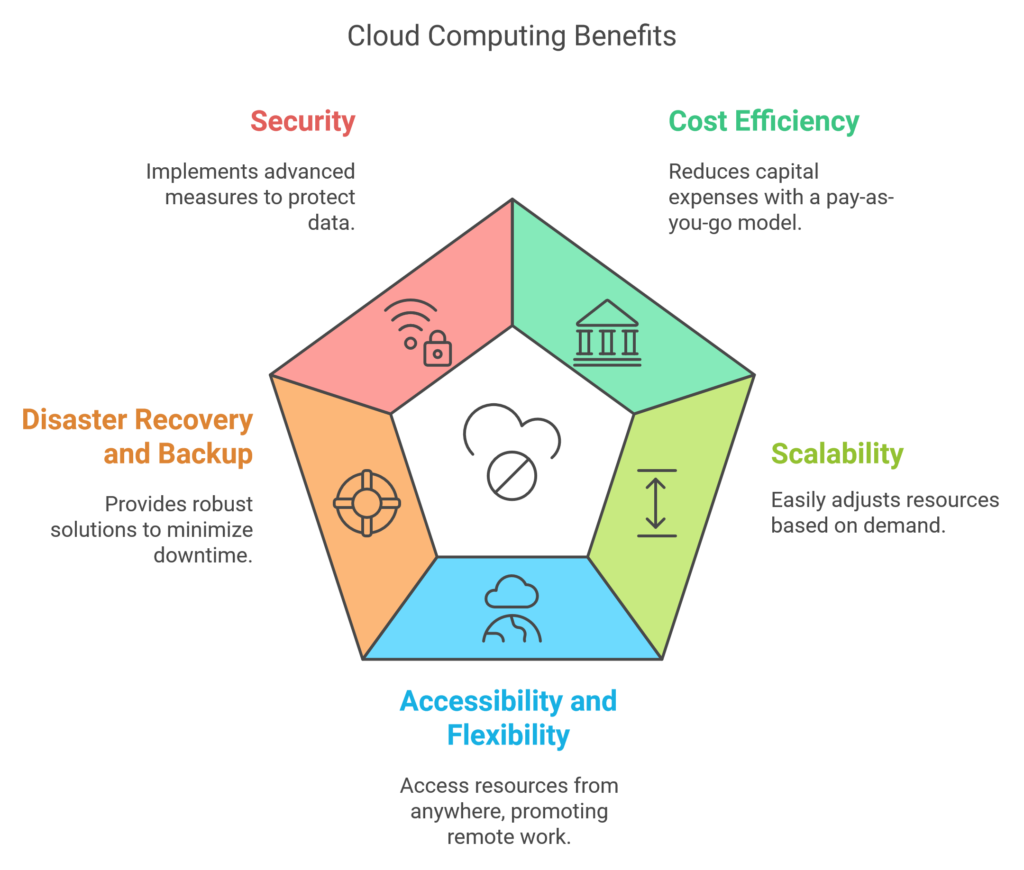
Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Cost Efficiency:
- Reduces the capital expense of buying hardware and software.
- Offers a pay-as-you-go model, minimizing costs by only paying for what you use.
- Scalability:
- Easily scale resources up or down based on demand, making it ideal for businesses with fluctuating workloads.
- Accessibility and Flexibility:
- Access resources from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting remote work and collaboration.
- Disaster Recovery and Backup:
- Provides robust backup and recovery solutions, reducing downtime in the event of a failure.
- Security:
- Leading cloud providers implement advanced security measures to protect data, including encryption and multi-factor authentication.
The Big Three: AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure
Now, let’s dive into the three most popular cloud computing platforms:
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Overview: AWS is the leading cloud services platform, launched by Amazon in 2006. It offers a wide array of cloud services, including computing power, storage, and machine learning.
Key Features:
- Extensive Service Portfolio: AWS provides over 200 services, including Amazon EC2 for virtual servers, Amazon S3 for storage, and AWS Lambda for serverless computing.
- Global Reach: With numerous data centers across the globe, AWS offers high availability and low latency.
- Strong Ecosystem: A vast network of partners, integrations, and support options.
Popular Use Cases:
- Hosting websites and applications.
- Big data analytics.
- Machine learning and artificial intelligence projects.
Pros:
- Wide range of services and features.
- Highly customizable and scalable.
- Strong focus on security and compliance.
Cons:
- Can be complex for beginners.
- Pricing can be challenging to understand.
2. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Overview: Google Cloud, launched in 2008, is known for its strong data analytics and machine learning capabilities, leveraging Google’s expertise in search and AI.
Key Features:
- Big Data and AI Tools: Services like BigQuery and Google Cloud Machine Learning Engine make GCP a favorite for data-driven projects.
- Kubernetes Expertise: Google created Kubernetes, an open-source container orchestration platform, and offers Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) for managing containers.
- Integration with Google Services: Seamless integration with other Google services like Google Workspace and Google Analytics.
Popular Use Cases:
- Data analysis and business intelligence.
- Hosting machine learning models.
- High-performance computing.
Pros:
- Excellent machine learning and data analytics capabilities.
- Competitive pricing with flexible options.
- Strong integration with open-source tools.
Cons:
- Smaller service portfolio compared to AWS and Azure.
- Less global presence in data centers.
3. Microsoft Azure
Overview: Launched in 2010, Azure is Microsoft’s cloud platform. It is popular among businesses that already use Microsoft products like Windows Server, SQL Server, and Office 365.
Key Features:
- Hybrid Cloud Capabilities: Azure offers robust hybrid cloud solutions, allowing seamless integration with on-premises environments.
- Enterprise-Ready: Strong focus on enterprise applications, with services like Azure Active Directory and Azure SQL Database.
- Integration with Microsoft Products: Deep integration with existing Microsoft tools, making it an attractive choice for businesses already using Microsoft software.
Popular Use Cases:
- Hosting Microsoft enterprise applications.
- IoT (Internet of Things) and edge computing.
- Developing and deploying web and mobile applications.
Pros:
- Excellent hybrid cloud support.
- Seamless integration with Microsoft products.
- Strong enterprise focus with a wide range of services.
Cons:
- Can be complex for non-Microsoft environments.
- Pricing can be high for certain services.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Platform
Selecting the right cloud platform depends on your business needs and technical requirements. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | AWS | Google Cloud | Azure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best For | Wide service variety, enterprise applications | Data analytics, AI, and machine learning | Microsoft integrations, hybrid cloud solutions |
| Ease of Use | Medium to Complex | User-friendly | Medium |
| Pricing | Flexible but complex | Transparent and competitive | Flexible, often higher for enterprise services |
| Global Reach | Extensive | Moderate | Extensive |
| Machine Learning | Strong | Strong | Good |
| Hybrid Cloud Capabilities | Moderate | Moderate | Strong |
Considerations When Choosing a Cloud Provider:
- Budget: Evaluate the cost-effectiveness based on your usage needs.
- Service Requirements: Identify the specific services your project requires, such as machine learning or data analytics tools.
- Integration Needs: If your organization uses specific tools (e.g., Microsoft products), choose a cloud provider that integrates seamlessly with them.
- Scalability: Ensure the platform can handle your projected growth in terms of traffic and data.
Getting Started with Cloud Computing
For beginners, it’s best to start small and gradually scale up as you become more familiar with cloud services. Here’s how to get started:
- Sign Up for a Free Tier: AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure all offer free tiers with access to several services. You can experiment with these at no cost to get a feel for the platform.
- Learn the Basics: Take advantage of free tutorials, documentation, and courses provided by each platform. Resources like AWS Training, Google Cloud Training, and Microsoft Learn are great starting points.
- Build a Simple Project: Start by building a basic project, such as a simple website or application, to understand how cloud services work in practice.
- Explore Certification Programs: Consider pursuing certifications like AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Google Cloud Associate Engineer, or Microsoft Azure Fundamentals to deepen your knowledge and enhance your credentials.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is transforming how businesses operate, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure each provide unique strengths, making them suitable for different use cases. By understanding the basics and exploring the services offered by these providers, beginners can harness the power of the cloud to drive innovation and growth.
Whether you’re a startup looking to scale quickly or an established business seeking to optimize costs, cloud computing can be a game-changer. With the right approach, you can leverage these powerful platforms to build, deploy, and scale your applications seamlessly.
